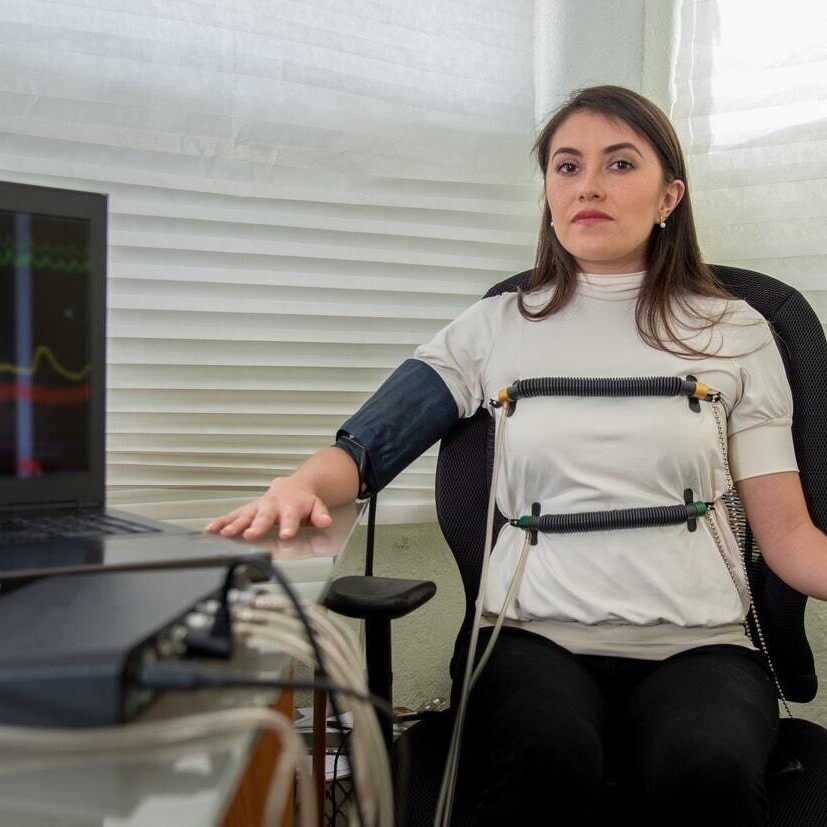
Over 75 years, there have been more than 250 studies on the accuracy of the Polygraph. The Department of Defence Polygraph Institute of the United States of America (DODPI) as well as the American Polygraph Association (APA) recently did a study of the accuracy of all other studies done. The average accuracy range was found to be in the region of 90-95%.Studies can be viewed at: www.polygraph.org/polygraph-validity-research
According to Dr David C. Raskin, the world-renowned expert and leading scientist in the field of polygraphy, the scientific data concerning the validity of the polygraph can be summarized as follows:
"High quality scientific research from the laboratory and the field converge on the conclusion that a properly conducted CQT (Comparison Question Test) is a highly accurate discriminator of truth tellers and deceivers. The research results converge on an accuracy estimate that exceeds 90 percent."
According to the American Polygraph Association (APA), 80 research projects, which included both laboratory and field studies, have been conducted and published since 1980 on the validity and reliability of polygraph testing. These projects involved approximately 6,300 polygraph examinations. Of the 23 field studies conducted, the accuracy of polygraph testing was estimated to be 95 percent.
Like any other diagnostic instrument that is used to measure human physiology for the purpose of evaluation and forming professional opinions thereupon, the polygraph instrument is not infallible. The relevant scientific community agrees, however, that polygraph examinations have a very high probative value in distinguishing truthful individuals from deceptive ones, and that no other alternative testing technique for truth verification and lie detection performs better.